Given the head of a singly linked list, return true if it is a
or false otherwise.
Example 1:
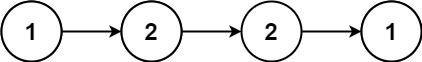
Input: head = [1,2,2,1] Output: true
Example 2:
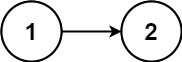
Input: head = [1,2] Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9
Follow up: Could you do it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
A:
就是简单的读2遍,然后一个从后往前,一个从前往后。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/class Solution {public:bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {// iterate twicevector<int> V;auto runner = head;while (runner) {V.push_back(runner->val);runner = runner->next;}runner = head;while (runner) {auto last = V.back();V.pop_back();if (last != runner->val) {return false;}runner = runner->next;}return true;}};
Follow up:
Could you do it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
1: reverse后半段。
2: 利用 recursive 的call stack,来对比
No comments:
Post a Comment