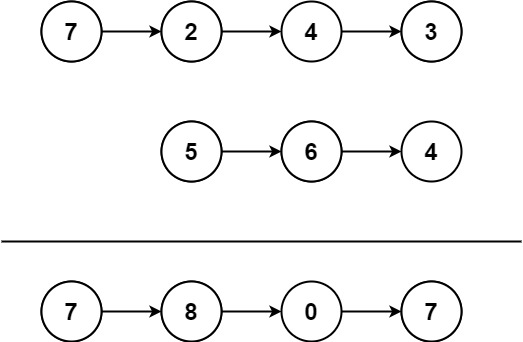
m and n with digits 0-9 representing two numbers. Create the maximum number of length k <= m + n from digits of the two. The relative order of the digits from the same array must be preserved. Return an array of the k digits. You should try to optimize your time and space complexity.[3, 4, 6, 5]nums2 =
[9, 1, 2, 5, 8, 3]k =
5return
[9, 8, 6, 5, 3][6, 7]nums2 =
[6, 0, 4]k =
5return
[6, 7, 6, 0, 4][3, 9]nums2 =
[8, 9]k =
3return
[9, 8, 9]就是每个寻找最大的(如果相同,则看下一位-----为了省事儿,我们先用递归的方式)
public class Solution {
public int[] maxNumber(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
int[] res = new int[k];
int i1=0, i2=0;// valid position
for(int i =0;i<k;i++){
// k - i is how many we need to find, (num2.length-i2) is how many others can provide
int maxIndex1 = getMaxIndex(nums1,i1, k - i - (nums2.length - i2) );
int maxIndex2 = getMaxIndex(nums2,i2, k - i - (nums1.length - i1) );
if(maxIndex1<0){
res[i] = nums2[maxIndex2];
i2 = maxIndex2+1;
continue;
}
if(maxIndex2<0){
res[i] = nums1[maxIndex1] ;
i1 = maxIndex1+1;
continue;
}
int max1 = nums1[maxIndex1], max2 = nums2[maxIndex2];
if( max1 > max2){
res[i] = max1 ;
i1 = maxIndex1+1;
}else if(max1 < max2){
res[i] = max2;
i2 = maxIndex2+1;
}else{ // max1 == max2
res[i] = max1;
// try to move the maxIndex1 by 1
int[] res1 = maxNumber(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums1, maxIndex1+1,nums1.length ),
Arrays.copyOfRange(nums2, i2, nums2.length ),
k-i-1);
// try the case that move the maxIndex2 forward
int[] res2 = maxNumber(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums1, i1,nums1.length ),
Arrays.copyOfRange(nums2, maxIndex2+1, nums2.length ),
k-i-1);
if(isFirstArrayBigger(res1,res2)){
for(int t = 0; t<res1.length; t++){ // might use the arrayCopyOfRange()
res[i+1+t] = res1[t];
}
}else{
for(int t = 0; t<res2.length; t++){ // might use the arrayCopyOfRange()
res[i+1+t] = res2[t];
}
}
break;
}
}
return res;
}
private int getMaxIndex(int[] A, int start,int leastNumberOfElementWeNeed){
if(A.length==0)
return -1;
int maxIndex = -1, maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i =start; i<= Math.min(A.length-1, A.length - leastNumberOfElementWeNeed); i++ ){
if(A[i]>maxValue){
maxIndex = i;
maxValue = A[i];
}
}
return maxIndex;
}
private boolean isFirstArrayBigger(int[] A, int B[]){// A and B are the same size
for(int i =0;i<A.length; i++){
if(A[i]>B[i])
return true;
if(A[i]<B[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
上面的超时了, 问题出在,如果相同的话,我们会实验两遍。因此不好看。
有没有更好的方法呢?????
再想想~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
嗯,利用这样一个特性:
0~~~~9 是确定的。因此我们可以把每个地址都记录下来。这样我们就不用一遍遍copy数组了。
Mistakes:
1: 编码的时候,忘记了,如果相同,则看下