A binary tree is univalued if every node in the tree has the same value.
Return true if and only if the given tree is univalued.
Example 1:
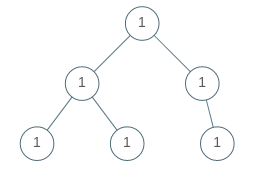
Input: [1,1,1,1,1,null,1] Output: true
Example 2:
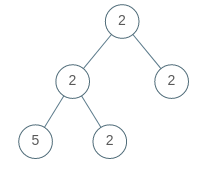
Input: [2,2,2,5,2] Output: false
Note:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 100]. - Each node's value will be an integer in the range
[0, 99].
A:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return true; return helper(root,root->val); } private: bool helper(TreeNode * root, const int val){ if(!root) return true; if(root->val != val) return false; if( ! helper(root->left, val)) return false; return helper(root->right, val); } };
No comments:
Post a Comment