Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example 1:
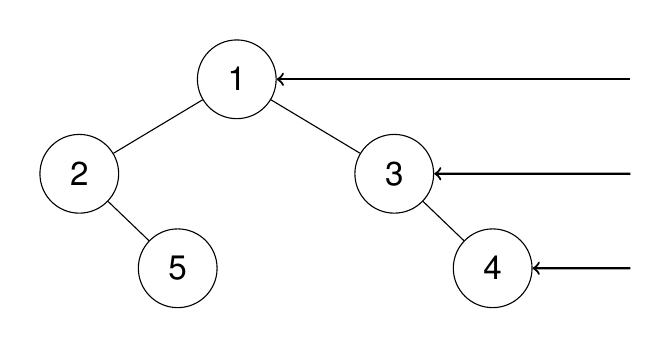
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]
Explanation:
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5]
Output: [1,3,4,5]
Explanation:

Example 3:
Input: root = [1,null,3]
Output: [1,3]
Example 4:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
A:
我所能想到的,就是简单的bfs (dfs)
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
if(root == null)
return list;
queue.add(root);
while( queue.isEmpty() == false){
Queue<TreeNode> newQueue = new LinkedList();
boolean isFirst = true;
while( ! queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(isFirst){
list.add(node.val);
isFirst = false;
}
if(node.right != null)
newQueue.add(node.right);
if(node.left != null)
newQueue.add(node.left);
}
queue = newQueue;
}
return list;
}
}
***********dfs ****************
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> res;helper(root, res, 0);return res;}private:void helper(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res, int curDepth) {if (!root)return;if (res.size() == curDepth)res.push_back(root->val);helper(root->right, res, curDepth + 1);helper(root->left, res, curDepth + 1);}};
Mistakes:
Learned:
No comments:
Post a Comment