You have a data structure of employee information, including the employee's unique ID, importance value, and direct subordinates' IDs.
You are given an array of employees employees where:
employees[i].idis the ID of theithemployee.employees[i].importanceis the importance value of theithemployee.employees[i].subordinatesis a list of the IDs of the direct subordinates of theithemployee.
Given an integer id that represents an employee's ID, return the total importance value of this employee and all their direct and indirect subordinates.
Example 1:
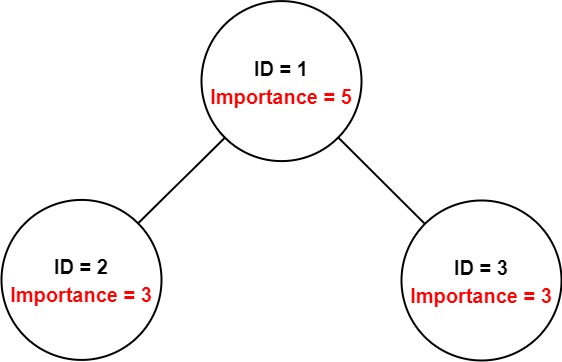
Input: employees = [[1,5,[2,3]],[2,3,[]],[3,3,[]]], id = 1 Output: 11 Explanation: Employee 1 has an importance value of 5 and has two direct subordinates: employee 2 and employee 3. They both have an importance value of 3. Thus, the total importance value of employee 1 is 5 + 3 + 3 = 11.
Example 2:
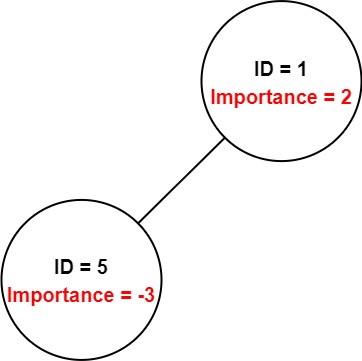
Input: employees = [[1,2,[5]],[5,-3,[]]], id = 5 Output: -3 Explanation: Employee 5 has an importance value of -3 and has no direct subordinates. Thus, the total importance value of employee 5 is -3.
Constraints:
1 <= employees.length <= 20001 <= employees[i].id <= 2000- All
employees[i].idare unique. -100 <= employees[i].importance <= 100- One employee has at most one direct leader and may have several subordinates.
- The IDs in
employees[i].subordinatesare valid IDs.
/*// Definition for Employee.class Employee {public:int id;int importance;vector<int> subordinates;};*/class Solution {public:int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {unordered_map<int, Employee*> M;for (auto e : employees) {M[e->id] = e;}int res = 0;queue<int> Q;Q.push(id);while (not Q.empty()) {auto idx = Q.front();Q.pop();res += M[idx]->importance;for (auto v : M[idx]->subordinates)Q.push(v);}return res;}};