Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest path, where each node in the path has the same value. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of the path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
Example 1:
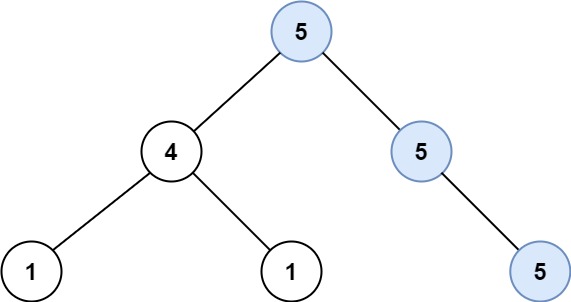
Input: root = [5,4,5,1,1,null,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 5).
Example 2:
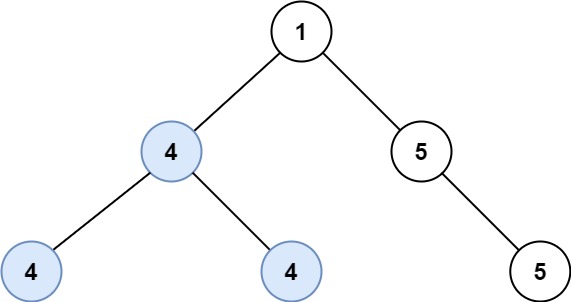
Input: root = [1,4,5,4,4,null,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 4).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000- The depth of the tree will not exceed
1000.
A:
第二遍。 主函数return的时候,没考虑空的情况,返回的是number of node,而不是length
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
helper(root, ans);
return max(0, ans - 1); // -1 because : it is length, not number of nodes
}
private:
// return the longest down-path lenght with the same value as root
int helper(TreeNode* root, int & ans){ // while update the longest Univalue path.
if(!root)
return 0;
int l = helper(root->left, ans);
int r = helper(root->right, ans);
int uniLeft = (root->left) ? ( root->val == root->left->val? l : 0 ):0;
int uniRight = (root->right) ? ( root->val == root->right->val? r : 0 ):0;
ans = max(ans, 1 + uniLeft + uniRight);
return 1 + max(uniLeft, uniRight);
}
};
*************第一遍---------要多写几遍, 一开始bug挺多的 ************
************* 而且有重复计算的问题 , 效果不是最好 **********
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) { if(root == nullptr) return 0; int withRootpath = 0; if(root->left != nullptr ) withRootpath += maxDepthWithValue(root->left, root->val); if(root->right != nullptr) withRootpath += maxDepthWithValue(root->right, root->val); return max(withRootpath , max(longestUnivaluePath(root->left),longestUnivaluePath(root->right))); } private: int maxDepthWithValue(TreeNode* root, const int value) { if(root ==nullptr || root->val != value) return 0; int res = 0; int ll = maxDepthWithValue(root->left, value); int rr = maxDepthWithValue(root->right, value); return 1 + max(ll, rr); } };
No comments:
Post a Comment