Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
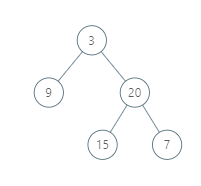
Example 1:
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] Explanation: Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0): Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1); The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2); The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1); The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
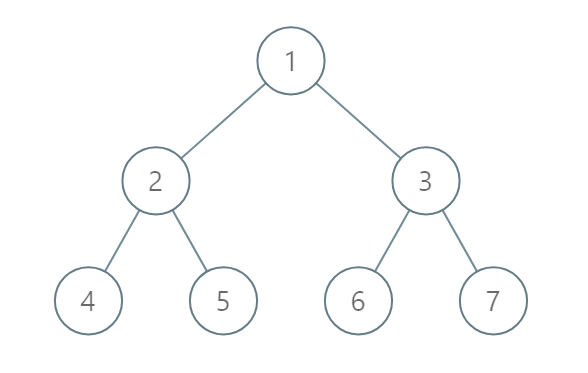
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] Explanation: The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme. However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
A:
就是先遍历,并存在一个sorted map 中 。然后再整理到最终结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) { map<int, vector<int>> M; // default sorted by increasing order of key dfs(root, M, 1001, 1001); // use 1000, instead of 0, to avoid dealing with negative when doing / vector<vector<int>> res; int preX = INT_MIN; // minus any number thus, when using it as index, we can simply add 1 for (auto& it : M) { if ( it.first / 1001 != preX / 1001) { preX = it.first; res.push_back(vector<int>()); } sort(it.second.begin(), it.second.end()); res.back().insert(res.back().end(), it.second.begin(), it.second.end()); } return res; } private: void dfs(const TreeNode* root, map<int, vector<int>>& M, int x, int y) { if (not root) return; M[x * 1001 + y].push_back(root->val);// at most 1000 node // use y+1 instead of y-1, so for same x value, we have sorted increasing y value dfs(root->left, M, x - 1, y + 1); dfs(root->right, M, x + 1, y + 1); } }; |
Learned:
use map to save the key (by default, C++ map is sorted by the increasing order of the key)
Mistakes :
Line 16, dfs(root, M, 1001, 1001); // use 1000, instead of 0, to avoid dealing with negative when doing / 我
一开始设root 的起始 为 0,0, 。 然而最终需要从 key 来计算 x 的时候,对于 (-1000, 0, 4 ) / 1001 . 他们的结果都是0 , 显然不是我们想要的。 这时候,我们或者用floor(-(double)1000 / 1001)
或者规避key 为负数的情况。(如code显示)
NOTE:
int a = -2, b = 1001; floor(a/b) == 0
double a = -2.0; int b = 1001; floor(a/b) == -1.
No comments:
Post a Comment