Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Example 1:
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
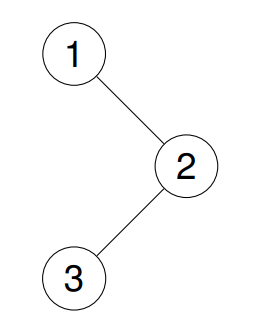
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]
Explanation:
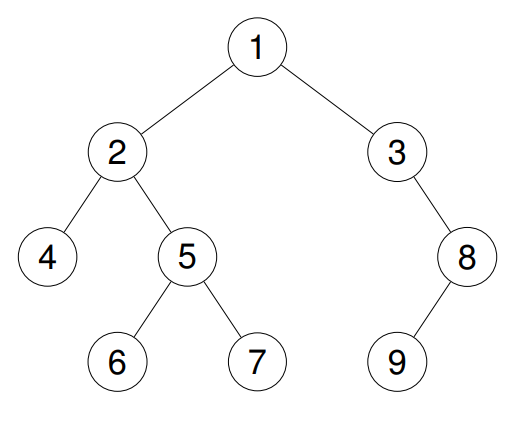
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
Output: [4,6,7,5,2,9,8,3,1]
Explanation:
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
A:
-----------------递归解法-----------
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
helper(root, res);
return res;
}
private:
void helper(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res) {
if (!root)
return;
helper(root->left, res);
helper(root->right, res);
res.push_back(root->val);
}
};
不论是用两个stack (还是每次加到前面,最后reverse回来)原理都是一样的。
Mistakes:
1: 忘了先check root为null 的情况
--------------------------第三遍------(用了一个stack,一个set(set来记录是否被visited过))--------------------
2: 把if写成了while , 哎,丢死人了
3: 写成了先 压栈右边,再压栈左边的了。 这个, 当时是考虑到正常顺序,是要先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树的。 但是, 但是,没有考虑到, 其实,我们是reversely 加入到al的最前面的。 因此, 要先遍历右子树的。
Learned:
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> res;stack<TreeNode*> S;if(root)S.push(root);while(!S.empty()){auto tmp = S.top();S.pop();res.push_back(tmp->val);if(tmp->left)S.push(tmp->left);if(tmp->right)S.push(tmp->right);}reverse(res.begin(), res.end());return res;}};
Mistakes:
1: 忘了先check root为null 的情况
--------------------------第三遍------(用了一个stack,一个set(set来记录是否被visited过))--------------------
2: 把if写成了while , 哎,丢死人了
3: 写成了先 压栈右边,再压栈左边的了。 这个, 当时是考虑到正常顺序,是要先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树的。 但是, 但是,没有考虑到, 其实,我们是reversely 加入到al的最前面的。 因此, 要先遍历右子树的。
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList();
if(root ==null)
return result;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
Set<TreeNode> set = new HashSet();
stack.push(root);
set.add(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(set.contains(node)){// first time to find this node
stack.push(node);
if(node.right!=null){
stack.push(node.right);
set.add(node.right);
}
if(node.left!=null){
stack.push(node.left);
set.add(node.left);
}
set.remove(node);
}else{// node should be printed directly
result.add(node.val);
}
}// end of while
return result;
}
}
Learned:
No comments:
Post a Comment