Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node p is the node with the smallest key greater than p.val.
Example 1:

Input: root = [2,1,3], p = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of TreeNode type.
Example 2:
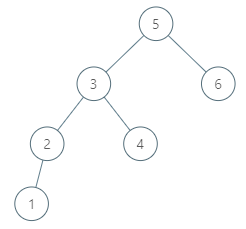
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer is null.
Note:
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return
null. - It's guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
A:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p) { if(not root or not p) return nullptr; if(root->val <= p->val){ return inorderSuccessor(root->right, p); }else{ auto tmp = inorderSuccessor(root->left, p); if(tmp){ return tmp; }else{ return root; } } } };
No comments:
Post a Comment