A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1:
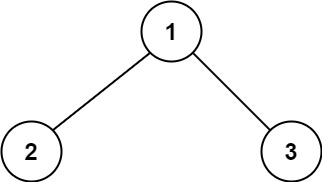
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: 6 Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
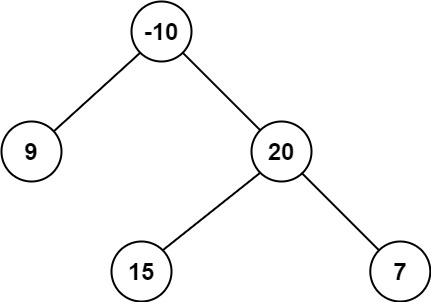
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 42 Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
---------------------------------3rd pass ----
传递一个可以引用的参数来记录最大的值。
返回的是该节点向下的最大值(最少一个节点)
或者我们允许左或右子树,可以没有节点。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) { // the path must go through a root node ofint res = INT_MIN;helper(root, res);return res;}private:int helper(TreeNode* root, int& res) { // root is always not NULLint maxL = 0, maxR = 0;if (root->left)maxL = helper(root->left, res);if (root->right)maxR = helper(root->right, res);res = max(res, root->val + max(0, maxL) + max(0, maxR));return root->val + max({0, maxL, maxR});}};
或者我们允许左或右子树,可以没有节点。
class Solution { public: int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) { int maxRes = INT_MIN; helper(root, maxRes); return maxRes; } private: int helper(TreeNode* root, int & maxRes){ if(! root) return 0; int maxLeft = helper(root->left, maxRes); int maxRight = helper(root->right, maxRes); int maxAtRoot = root->val + maxLeft + maxRight; maxRes = max(maxRes, maxAtRoot); return max(0, root->val + max(maxLeft, maxRight) ); } };
-------------------------------------1 st round -----------------------------------------
很简单的思路:
因为,必须有一个节点作为root(最少选一个节点,只要树不空,就不能不选) 。 那么,也就有且只有一个节点。 我们因此,只需要检测,通过每一节点的最大path sum 就可以了。
public class BinaryTreeMaximumPathSum {
// Improvement : record the maxPathDown value of each node;
// in this way, we need to build another treeNode class to record maxValue
// NOTE: the hidden philosophy is : we have only one
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
// recursively calling, to build the new tree
TreeNode2 root2 = buildTree2(root);
// traversal root2, to find the max path rooted at each node
int[] res = new int[1];
res[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
getMaxPathSum(root2, res);
return res[0];
}
private void getMaxPathSum(TreeNode2 root, int[] res) {// root must be
// included
// get the max paths sum at root, and then search child
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
int curPathSum = root.maxPathUpHere;
res[0] = Math.max(res[0], curPathSum);
return;
}
if (root.left != null && root.right == null) {
res[0] = Math.max(res[0], root.maxPathUpHere);
getMaxPathSum(root.left, res);
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {
res[0] = Math.max(res[0], root.maxPathUpHere);
getMaxPathSum(root.right, res);
return;
}
// NOW, both children are not null
int curPathSum = root.val + Math.max(0, root.right.maxPathUpHere)
+ Math.max(0, root.left.maxPathUpHere);
res[0] = Math.max(res[0], curPathSum);
getMaxPathSum(root.left, res);
getMaxPathSum(root.right, res);
return;
}
private TreeNode2 buildTree2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode2 root2 = new TreeNode2(root);
root2.left = buildTree2(root.left);
root2.right = buildTree2(root.right);
int maxLeft = 0;
if (root2.left != null && root2.left.maxPathUpHere > 0)// we can do not
// count it
maxLeft = root2.left.maxPathUpHere;
int maxRight = 0;
if (root2.right != null && root2.right.maxPathUpHere > 0)
maxRight = root2.right.maxPathUpHere;
root2.maxPathUpHere = root2.val + Math.max(maxLeft, maxRight);
return root2;
}
class TreeNode2 {
int val;
TreeNode2 left, right;
int maxPathUpHere = 0; // max sum to to current node
TreeNode2(TreeNode node) {
val = node.val;
}
}
}
------------------第二遍, 不用重新创立一个tree----------- 就直接更改原有的treeNode.val-----方法就是传递,并返回一个数组 因此,对一个TreeNode nodeA 检测的时候,我们要返回
int res[] = new int[2]
res[0] : maximim path sum, up to nodeA (inclusive) or 0 ( if former < 0)
res[1] : maximim path sum , rooted at nodeA ( inclusive)
public class Solution {
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
int[ ] res = getMaxPathSum(root);
return res[1];
}
private int[] getMaxPathSum(TreeNode root){
// res[0] is the up-to-node max-sum, current node must be included
// res[1] is the max-sum of a tree, rooted this node
int[] res = { Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE };
if (root == null)
return res;
int[] left = getMaxPathSum(root.left);
int[] right = getMaxPathSum(root.right);
res[0] = root.val + Math.max(0, Math.max(left[0], right[0]));
int maxOfChild = Math.max(left[1], right[1]);// max sum of path
int maxSumThroughRoot = Math.max(0,left[0]) + root.val + Math.max(0, right[0]);
res[1] = Math.max(maxOfChild, maxSumThroughRoot);
return res;
}
}
Mistakes:
1: 必须找到一条路径,不能不找。 --------->
Learned:
1: leetcode的run time error 多为:
1)print了东西
2) 99%是你deference null pointer了,
endless loop则会提示Time limit exceeded。
3)数组越界,除0,爆栈,访问空地址
4) leetcode中,不好用static int 来存储变量。 那么,我们可以声明一个数组, int res[] = int [1]. 然后,就传这个数组就可以了。
No comments:
Post a Comment