Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
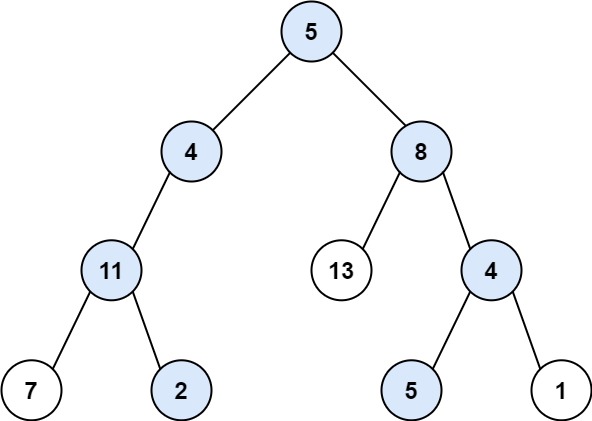
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]] Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum: 5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22 5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {vector<int> tmp;vector<vector<int>> res;helper(root, targetSum, tmp, res);return res;}private:void helper(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, vector<int> & tmp, vector<vector<int>> & res){if(!root)return;tmp.push_back(root->val);targetSum -= root->val;if(!root->left && !root->right){ // is leaf nodeif(targetSum == 0){res.push_back(vector<int>(tmp));}}helper(root->right, targetSum, tmp, res);helper(root->left, targetSum, tmp, res);tmp.pop_back();}};
Mistakes:
1: 当到了leaf节点,并且相等的时候,忘了返回, 艹
2: ,当不满足的时候,要返回空,而不是null。
------------------------第二遍-----------------
和第一遍不一样的地方就在于, 重新弄了一个函数, 把all 作为参数传过去了。
No comments:
Post a Comment