Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
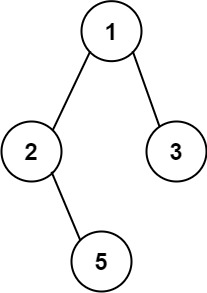
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: ["1"]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
递归,同时传入路径作为String参数
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),* right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {vector<string> V;helper(root, V, to_string(root->val));return V;}private:void helper(TreeNode* root, vector<string>& V,string pre) { // root is not nullif (!root)return;if (!root->left && !root->right) {V.push_back(pre);}if (root->left) {helper(root->left, V, pre + "->" + to_string(root->left->val));}if (root->right) {helper(root->right, V, pre + "->" + to_string(root->right->val));}}};
*************2nd pass**********没有用helper Function*********
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {// root is not NULL
vector<string> V;
if(!root->left && ! root->right){
V.push_back(to_string(root->val));
}
if(root->left){
auto leftRes = binaryTreePaths(root->left);
for(auto s: leftRes){
V.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + s);
}
}
if(root->right){
auto rightRes = binaryTreePaths(root->right);
for(auto s: rightRes){
V.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + s);
}
}
return V;
}
};
********Iteratively, using a stack ****************
但是这样,需要考虑该节点只有一个child 都情况,因此需要判断其有几个child。
No comments:
Post a Comment