Given the root of a binary tree, return the most frequent subtree sum. If there is a tie, return all the values with the highest frequency in any order.
The subtree sum of a node is defined as the sum of all the node values formed by the subtree rooted at that node (including the node itself).
Example 1:
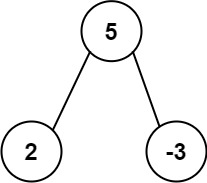
Input: root = [5,2,-3] Output: [2,-3,4]
Example 2:
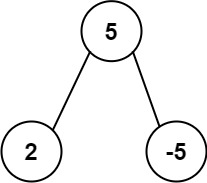
Input: root = [5,2,-5] Output: [2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
A:
就是递归调用,并把结果存在 map里
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<int> findFrequentTreeSum(TreeNode* root) {unordered_map<int,int> M;helper(root, M);int maxCount = 0;for(const auto p : M){maxCount = max(maxCount, p.second);}vector<int> res;for(const auto p : M){if(p.second == maxCount){res.push_back(p.first);}}return res;}private:int helper(TreeNode* root, unordered_map<int,int> & M){if(!root)return 0;int l = helper(root->left, M);int r = helper(root->right, M);int sum = l + r + root->val;M[sum] +=1;return sum;}};
No comments:
Post a Comment